On Reddit, many naive Amazon sellers ask, “What is Amazon FBA?” and how this concept works. In short, Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a program where Amazon handles storage, packing, shipping, and customer service for sellers.
Overall, this offloads logistics from the seller, but the seller must have its own fulfillment center as well as handle the Amazon fees and requirements. In this complete guide, we’ll explain how Amazon FBA works and why it matters for sellers.
Read on to know how to get started as a seller and optimization strategies. Stay till the end to learn everything about Amazon FBA from the ground up.
What is Amazon FBA, and Why Does It Matter for Sellers?
Amazon officially defines FBA as a program that lets sellers outsource order fulfillment to Amazon. Sellers send inventory into Amazon’s fulfillment network, and they pick, pack, and ship orders. In effect, FBA turns Amazon’s logistics system into your warehouse and shipping team.
Read this detailed guide to learn if Amazon FBA is worth your time and money.
Why Does Amazon FBA Matter for Sellers?
Amazon FBA impacts sellers in several concrete ways:
- Prime Shipping Eligibility: FBA products qualify for Amazon Prime’s free two-day shipping, which boosts sales by increasing customer trust and conversion.
- Outsourced Logistics: Amazon handles inventory storage, packing, shipping, and returns for FBA orders, saving sellers substantial time, effort, and overhead.
- Buy Box and Visibility: FBA listings often rank higher in search results and are more likely to win Amazon’s Buy Box (the featured offer), significantly increasing sales.
- Reduced Overhead: FBA offloads warehousing and shipping costs onto Amazon, so sellers don’t need to maintain their own inventory facilities or pack orders, simplifying operations and costs.
How Does Amazon FBA Work? A Complete Guide
Getting started with Amazon FBA involves several key steps. After getting an introduction to Amazon FBA, understand this detailed process to learn how to increase sales:
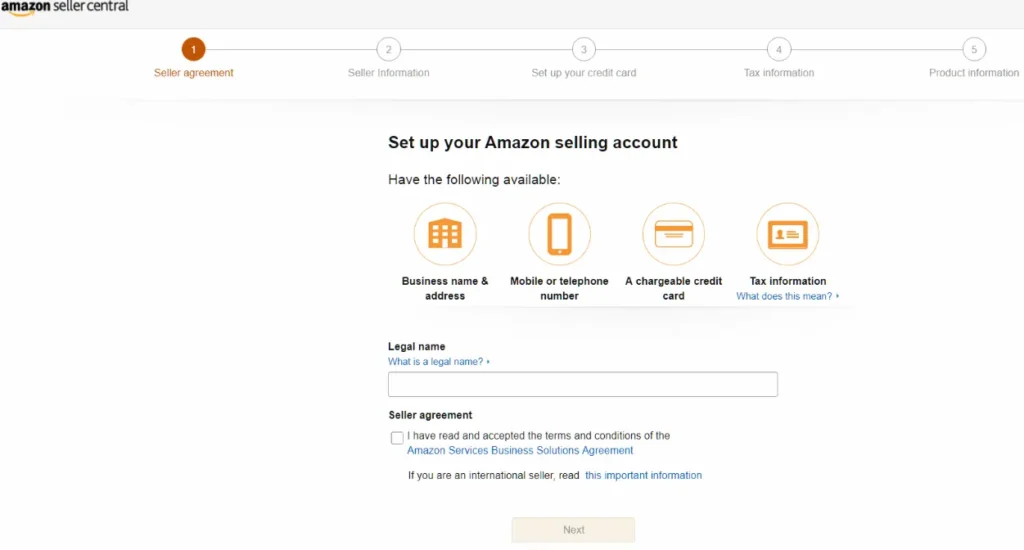
Step 1. Sign Up and Register for FBA
First, create an Amazon Seller Central account. You can choose an Individual or Professional selling plan. Once your account is set up, go to Account Info in Seller Central and select Register for FBA.
Step 2. Add Products to FBA
Next, list the products you want to sell. In each product listing, choose “Change to Fulfilled by Amazon” (or convert an existing listing to FBA). When you enroll a product in FBA, Amazon auto-generates a unique FNSKU barcode for that item.
Step 3. Prepare and Label Inventory
Before shipping inventory, prepare it to Amazon’s standards. Each item needs an FNSKU barcode label, as covered in our FNSKU guide. Follow Amazon’s packaging rules and then pack your products securely in boxes with proper shipping labels.
Step 4. Ship Inventory to Amazon
Use the “Send to Amazon” workflow in Seller Central to create a shipment plan. Enter your box details and choose a shipping method. You can use Amazon’s partnered carriers for discounted rates or pallet shipments for large volumes. Print shipping labels and ship the boxes to the designated Amazon fulfillment center.
If box dimensions or weight exceed Amazon’s limits, you’ll incur extra charges or even shipment rejections. Read this guide to learn about the Amazon FBA box size limit for sellers.
Step 5. Amazon Receives and Fulfills Orders
Once your inventory arrives, Amazon checks it in and stores it. From that point, when a customer orders one of your products, Amazon picks the item, packs it in an Amazon box, and ships it to the customer.

Explore this guide to learn about the Amazon Fulfillment Center in detail.
Step 6. Manage and Replenish Stock
Use Seller Central’s FBA Inventory dashboards to monitor stock levels. Watch your inventory health and set Replenishment Alerts to avoid stockouts. Amazon provides the FBA Restock Inventory tool to analyze your sales history and suggest how much inventory to send next.
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Amazon FBA?
Once sellers understand how Amazon FBA works, they need to weigh its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s examine the main pros and cons of using Fulfillment by Amazon.
Pros of Using Amazon FBA
The following are some of the major benefits of this program:
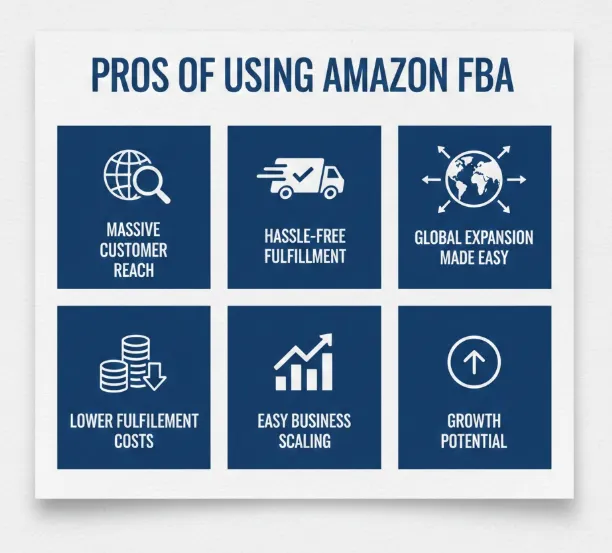
- FBA exposes your products to Amazon’s huge audience, leveraging the Amazon network to attract more buyers and significantly increase sales.
- Amazon expertly manages storage, packing, shipping, and returns for FBA orders to make inventory handling effortless.
- FBA lets you tap into Amazon’s worldwide fulfillment centers, enabling easy expansion into international markets and faster cross-border sales.
- Amazon FBA consolidates warehousing, packing, and shipping under one service. By using Amazon’s scale, many sellers find that per-unit fulfillment costs are lower than doing it all themselves.
- With Amazon handling logistics, you can grow with fewer staff and less infrastructure. Sellers can focus on branding and new products while expanding inventory without worrying.
Cons of Using Amazon FBA
When you get into the Amazon FBA program details, you will observe these drawbacks
- Amazon charges various fees for FBA (referral fees, fulfillment fees, storage fees). These can add up, which significantly cuts into margins.
- Products may be lost or damaged in Amazon’s warehouses. Amazon’s reimbursement policy (especially after the March 2025 changes) often pays only the product’s manufacturing cost.
- If your items sit unsold, you’ll pay monthly storage fees and possibly hefty long-term storage fees. Any inventory that sits in Amazon’s warehouse for an extended period incurs significant monthly or long-term storage charges.
- With FBA, Amazon controls much of the fulfillment process. You have limited say over packaging and branding, and you can’t customize the unboxing experience.
- Amazon enforces detailed packaging and prep rules. Failing to comply (wrong box sizes, missing labels) can lead to shipment delays or extra fees.
How Sellers Can Get Started with Amazon FBA?
As a seller, you need to follow this Amazon FBA beginner guide to get started.
Step 1. Choose a selling plan (Individual or Professional) and register as a seller.
Step 2. In Seller Central, go to Account Info and click Register for FBA.
Step 3. Decide whether to use FBA for all products or just some. You can even use Multi-Channel Fulfillment to ship orders from other platforms through Amazon’s network.
Step 4. Now, list new products with FBA selected, or convert existing listings to “Fulfilled by Amazon”. Each FBA listing gets an FNSKU code for tracking.
Step 5. Once you have FBA orders flowing, focus on marketing, advertising, and expanding your catalog. Programs like Subscribe & Save or regional FBA can help scale sales.
Read this guide on how to sell on Amazon to improve your revenue flow.
What are the Costs and Fees Associated with Amazon FBA?
After learning “What is Amazon FBA” and how it works, let’s get into the details of its fee types:
Referral Fees
Amazon takes a commission on each sale, called a referral fee. This is a percentage of the item’s sale price (typically 5 to 15% depending on category). For example, electronics often have an 8% referral fee, and clothing has around 17% of the sale.
Fulfillment Fees (per unit)
For each FBA order, Amazon charges a fulfillment fee to cover picking, packing, and shipping. This fee depends on the item’s size and weight. For example, small items might cost around $2.50 to $3.50 per unit, while heavier or oversized items incur higher fees.
Storage Fees
You pay monthly storage fees based on the volume of your inventory in Amazon’s warehouses. Rates are typically around $0.75 to $0.87 per cubic foot off-peak, rising to around $2.40 in peak (holiday) months. If inventory sits longer than 365 days, additional long-term storage fees apply.
Other Service Fees
There are several other possible fees:
- Labeling and Prep Fees
- Removal and Disposal Fees
- Return Processing
- Account Subscription Fees ($0.99/item for Individual, $39.99/month for Professional)
How to Calculate Cost with the FBA Revenue Calculator?
To estimate profitability, Amazon provides a free FBA Revenue Calculator. By entering a product’s dimensions, weight, and price, you can compare expected Amazon fees versus fulfilling orders yourself. The calculator shows a breakdown of referral, fulfillment, and storage fees. This helps you decide if FBA makes financial sense.
You can get a free Amazon PPC audit from here to cut down on the fees.
What Optimization Strategies Can You Use for Amazon FBA?
Once you’re using FBA, certain strategies can maximize your profits on Amazon:
- Reducing Storage Fees: Maintain high inventory turnover to avoid long-term storage charges. Use the FBA Restock tool and inventory health reports to identify slow-moving items and remove excess stock.
- Inventory forecasting: Analyze past sales and seasonality to predict demand. Accurate forecasting lets you plan shipments so you neither stock out nor overstock.
- Restocking and Replenishment: Set replenishment alerts in Seller Central. These alerts notify you when stock for a product is running low. Coupled with the FBA Restock tool recommendations, you can automate when and how much to ship.
- Listing SEO and PPC advertising: Optimize your product listings with relevant keywords in the title, bullets, and description to improve organic ranking. Complement organic SEO with Amazon Sponsored Ads (PPC) management services.
How Can You Compare FBA vs. Other Fulfillment Models?
While getting into the Amazon FBA program details, let’s compare Amazon FBA with FBM and Dropshipping. The table below highlights key differences:
| Factor | Amazon FBA | FBM (Merchant) | Dropshipping |
| Inventory | Seller buys bulk inventory and ships it to Amazon’s warehouses. | Seller buys/stores inventory in their own facility or 3PL. | No upfront inventory (order product from supplier on demand). |
| Fulfillment | Amazon stores, packs, and ships each order. | Seller handles packing and shipping. | Supplier ships directly to customers after the order. |
| Startup Costs | High (must fund inventory purchases plus Amazon’s monthly fees) | Moderate (fund inventory and possible warehousing) | Low (little or no inventory purchase) |
| Profit Margins | Potentially higher volume, but Amazon’s fees cut into margins | Potentially higher (no FBA fees) | Slimmer |
In short, FBA is best when you want Amazon to handle logistics and can invest in inventory for fast Prime shipping. Dropshipping minimizes upfront costs since you buy only after a sale, as explained in the Amazon FBA vs. Dropshipping guide.
On the other hand, FBM keeps costs lower (you handle shipping) and offers full control, but lacks Prime eligibility and shifts all workload to you.
Conclusion
All in all, Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a powerful option for many sellers, as it lets you benefit from Prime shipping and Amazon’s logistics. However, you need to learn how Amazon FBA works and its associated costs before using this program.
Sellers even need to analyze its pros and cons prior to subscribing to the seller program by Amazon. Once you choose to enroll in the Amazon FBA program, scale your business by partnering with Amazon Aggregators and PPC management services like Impact Wolves.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Amazon FBA suitable for all businesses?
Not really, FBA only works best for sellers with strong product demand and enough capital to invest in inventory. It’s ideal for new or small businesses wanting to offload logistics. However, businesses with very low-margin items or highly seasonal items may find FBA’s fees and rules less suitable.
Do I need a Professional selling plan to use FBA?
No, any seller plan can use FBA. New sellers on the Individual plan (pay-per-item fee) or existing sellers on the Professional plan ($39.99 per month) can enroll in FBA.
How much should beginners invest in FBA?
The investment mostly varies by product. Budget for inventory costs (buying enough units to sell), shipping that inventory to Amazon, and Amazon fees. Beyond fees, you should start with at least enough inventory for your first 50 to 100 sales, which often means a few thousand dollars depending on the product.
Can anyone become an FBA seller?
Yes, any Amazon seller with a valid account can use FBA, regardless of plan. Before sending inventory, you must ensure your products meet Amazon’s FBA requirements, and you agree to FBA policies.